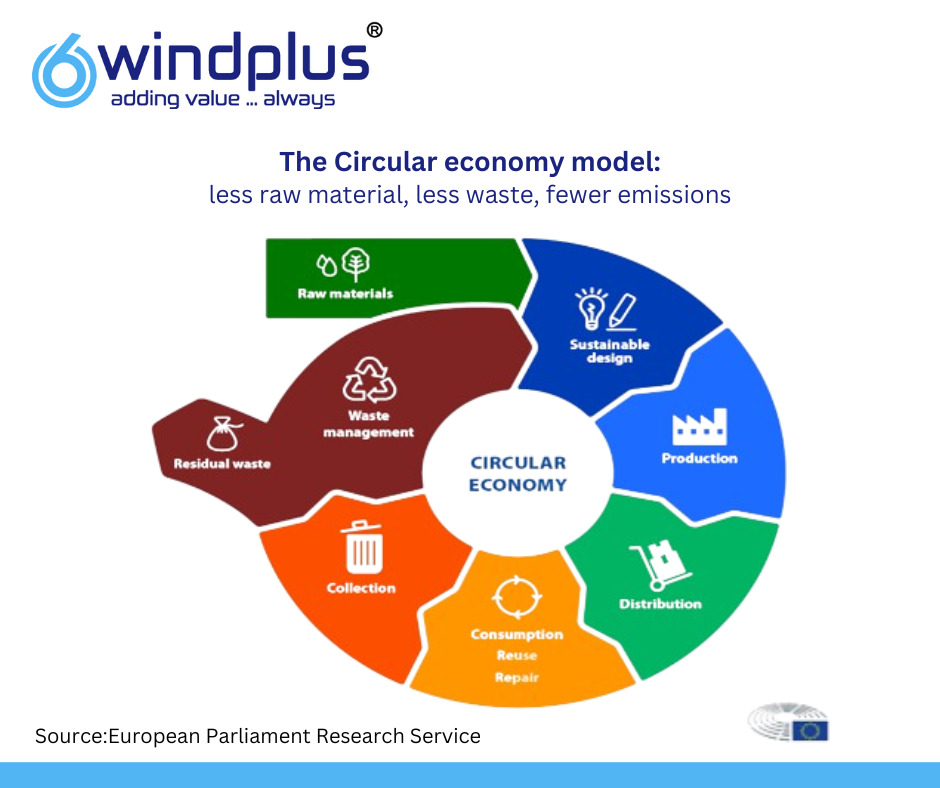
Recyclability is an important aspect for future wind turbines but before we dive into the topic, it is important to get an idea of the bigger picture – the concept of Circular Economy. So, what is circular economy and why is it important going forward?
Circular economy is a concept of production and consumption centered around three basic principles : Reduce, Reuse and Recycle. The aim of this idea is so that sustainable production is achieved by reusing waste efficiently and extending the value of products at end of life. This is of paramount importance in the long run since over-exploitation of Earth’s resources will result in shortage of raw materials needed to manufacture a product. Furthermore, pursuing this approach will lead to reduced greenhouse emissions, landscape degradation and biodiversity loss, all of which are key to maintaining a healthy environmental balance.
One of the many objectives of blade design is to achieve high strength to weight ratio to ensure structural stability during operation as shown in the above video. This applies to all modern wind turbines where the blade is layered with different materials such as composites, polymers and wood to achieve this. The materials collectively form a polymer based fiber-reinforced composite following the resin infusion process. Once end of life is reached, separating these materials from the resin becomes a major challenge and the most notable one here should be the fiberglass since it is non-biodegradable and not completely recyclable. Its complex structure of very fine layers of glass and plastic firmly bound to each other making it very difficult to break down. Due to this reason, majority of the blades end up being incinerated or in landfills after reaching end of life, thereby leaving a carbon footprint.
In order to tackle this problem at its source, manufacturers have devised new methodologies to enable recycling of wind turbine blade materials. Projects such as RecyclableBlade pioneered by Siemens Gamesa as well as DecomBlades, ZEBRA and Blades2Build involving LM Wind Power put the spotlight on effective processing and utilization of waste from decommissioned blades to ensure they can be reused in the future for alternate purposes. While research is still ongoing in this area, the rapid scaling and implementation of this technology has paved the way for future wind turbines to become completely recyclable so that they can be repurposed for alternate usage, some of which are displayed below. Additionally, the blades can also be used for making cement, furniture, building bridges and sound insulation materials.