In today’s world, SCADA system controls the entire manufacturing process in real-time. It is a control system that comprises of computers, network infrastructures, GUI, PLCs and RTUs.
Who Uses SCADA?
SCADA systems are used by industrial organizations and companies in the public and private sectors to control, monitor and maintain efficiency, distribute data for smarter decisions, and communicate system issues to help mitigate downtime. SCADA systems work well in many different types of enterprises because they can range from simple configurations to large, complex installations. SCADA systems applications are the backbone of many modern industries in,
- Energy Sector
- Food and beverage
- Manufacturing
- Oil and gas
- Power
- Recycling
- Transportation
- Water Management
- And many more
Some Examples are:
In Energy Sector, Electric power generation, transmission and distribution:
Electric utilities detect current flow and line voltage, to monitor the operation of circuit breakers, and to take sections of the power grid online or offline.
Manufacturing:
manage parts inventories for just in time manufacturing, regulate industrial automation and robots, and monitor process and quality control.
Mass transit:
regulate electricity to subways, trams and trolley buses; to automate traffic signals for rail systems; to track and locate trains and buses; and to control railroad
Traffic signals:
regulates traffic lights, controls traffic flow and detects out-of-order signals.
Buildings, facilities and environments:
Facility managers use SCADA to control HVAC, refrigeration units, lighting and entry systems.
Water and sewage:
State and municipal water utilities use SCADA to monitor and regulate water flow, reservoir levels, pipe pressure and
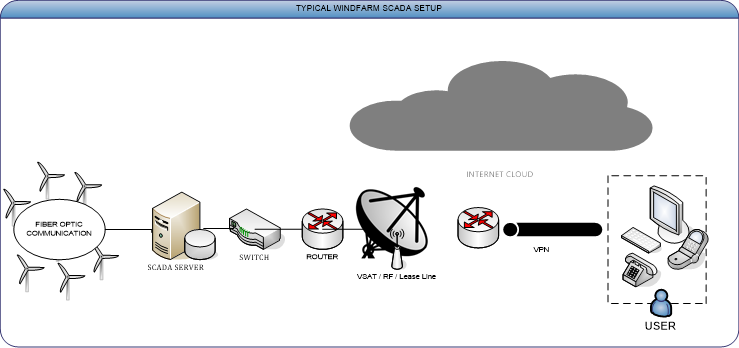
Basic operation of SCADA in Wind Power Plant:

- SCADA in Wind Power Plants Performs four Functions
- Monitoring the WTG
- Controlling the WTG
- Networked Data Communication
- Data Acquisition
These functions are performed by four kinds of SCADA Components
1. Sensors
Digital and Analog sensors to Sense the WTG parameters.
2. Controller
Each WTG is having a main controller unit/PLC/TRU that serve as local collection points for gathering reports from sensors and delivering commands to control relays

3. SCADA Server
These are larger computer consoles that serve as the central processor for data storage, control and the SCADA system. Master units provide a human interface to the system and automatically regulate the managed system in response to sensor inputs.
4. Communication Network
Connects the SCADA Server with Main Controller.